Autonous Vehicles are one of the most impactful innovations in terms of directly changing the way we work and live. The development of autonomous driving technology is commonly categorized into five levels:
- Level 0 (No Automation): The driver performs all driving tasks.
- Level 1 (Driver Assistance): The vehicle is controlled by the driver, but some driving assist features may be included in the vehicle’s design.
- Level 2 (Partial Automation): The vehicle has combined automated functions like acceleration and steering, but the driver must remain engaged with the driving task and monitor the environment at all times.
- Level 3 (Conditional Automation): The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under certain conditions, but the driver must be ready to take control when requested.
- Level 4 (High Automation): The vehicle can perform all driving tasks and monitor the driving environment in certain circumstances. The driver may have the option to control the vehicle.
- Level 5 (Full Automation): The vehicle can perform all driving tasks, under all conditions, without any human intervention.
Currently, it is considered that levels up to level 3 are almost being realized. Towards the realization of Full Automation, there are still challenges that remain difficult to resolve.
Development Companies
Waymo (a subsidiary of Google/Alphabet)
- Latest Developments: Waymo is a pioneer in autonomous driving technology, focusing particularly on Level 4 autonomy. It has launched a public self-driving taxi service called “Waymo One” in Phoenix, Arizona, and plans to expand its services to other cities. Additionally, through its “Waymo Via” division, it is advancing the development and testing of autonomous trucks for logistics.
Tesla
- Tesla offers “Autopilot” and the “Full Self-Driving (FSD)” package, with a significant focus on developing FSD. Elon Musk has repeatedly predicted the imminent realization of full autonomy, though as of now, Tesla has not achieved Level 5 autonomy. Tesla continuously improves its system and adds new features through extensive over-the-air updates.
Cruise (a subsidiary of General Motors)
- Cruise has been conducting pilot tests of its autonomous taxi service in San Francisco, offering rides to passengers on public roads during the night in a limited capacity. Cruise also has plans to expand its operations to other cities.
Baidu
- The Chinese tech giant Baidu is developing its autonomous driving technology, “Apollo”. Baidu has launched its robotaxi service “Apollo Go” in several Chinese cities, including Beijing, Guangzhou, and Changsha, and is expanding its service areas. Baidu has also developed an autonomous bus called “Apolong”.
Argo AI
- Argo AI, which had received backing from Ford and Volkswagen, closed its operations towards the end of 2022. The technology and talent from Argo AI have been absorbed by other companies and projects, contributing to the development of autonomous driving technologies.
Mobileye (a subsidiary of Intel)
- Mobileye specializes in vision-based sensor technology for autonomous driving. The company has formed partnerships with several automakers to commercialize its autonomous driving systems. Mobileye has also been testing its autonomous taxi service in Israel, with plans for expansion to other regions.
Additionally, Apple has announced that it will withdraw from the development of autonomous driving cars.
Elemental technology
Sensors and Perception Systems
Autonomous vehicles rely on a complex array of sensors to interpret their surroundings. These sensors include:
- Cameras: Provide visual information similar to what a human driver sees. They are crucial for recognizing traffic signs, signals, road markings, and other vehicles.
- LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): Emits laser beams to measure distances and create high-resolution maps of the vehicle’s surroundings. LIDAR is excellent for detecting the shape and distance of objects, even in low light conditions.
- Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging): Uses radio waves to detect the distance and speed of objects. Radar is particularly effective in adverse weather conditions, such as rain or fog, where optical sensors might struggle.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: Often used for close-range detection tasks, such as parking assistance. They can detect the proximity of objects to the vehicle’s body.
These sensors feed data into the vehicle’s perception system, which uses advanced algorithms to interpret the data, identify objects (like cars, pedestrians, and bicycles), and understand the vehicle’s environment.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are at the heart of autonomous driving systems, enabling vehicles to make decisions and learn from experience. Key areas include:
- Computer Vision: Allows the vehicle to understand and interpret visual information from cameras, enabling it to recognize traffic signs, signals, andcぃcきんg other important visual cues.
- Deep Learning: A subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with many layers. It is crucial for processing the vast amounts of data from the vehicle’s sensors and making real-time driving decisions.
- Path Planning and Decision Making: AI algorithms determine the best path and make decisions on speed, lane changes, and maneuvers based on the vehicle’s current environment, destination, and traffic laws.
Connectivity and V2X Communication
Connectivity plays a vital role in enhancing the capabilities of autonomous vehicles through:
- Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) Communication: Enables vehicles to communicate with each other (V2V), with infrastructure (V2I), with pedestrians (V2P), and with the network (V2N). This communication can improve safety and traffic efficiency by sharing information about traffic conditions, hazards, and vehicle intentions.
Software and Cybersecurity
Autonomous vehicles are powered by sophisticated software that integrates data from sensors, makes decisions, and controls the vehicle. This software must be regularly updated and protected against cyber threats. Cybersecurity is critical to protect the vehicle from hacking and ensure the safety and privacy of data.
Simulation and Testing
Before deployment, autonomous vehicles undergo extensive testing in simulated environments and controlled real-world conditions. Simulation allows developers to test vehicles in a wide range of scenarios, including rare and dangerous situations, without putting anyone at risk.
In summary, the development of autonomous driving technology involves the integration of advanced sensors, AI and machine learning for data processing and decision-making, connectivity for enhanced communication, and rigorous testing to ensure safety and reliability. These technologies collectively enable vehicles to navigate complex environments and make safe driving decisions without human intervention.
Innovation Maps
Here is an Innovation Map on Autonomous Vehicle from Journals of IEEE.
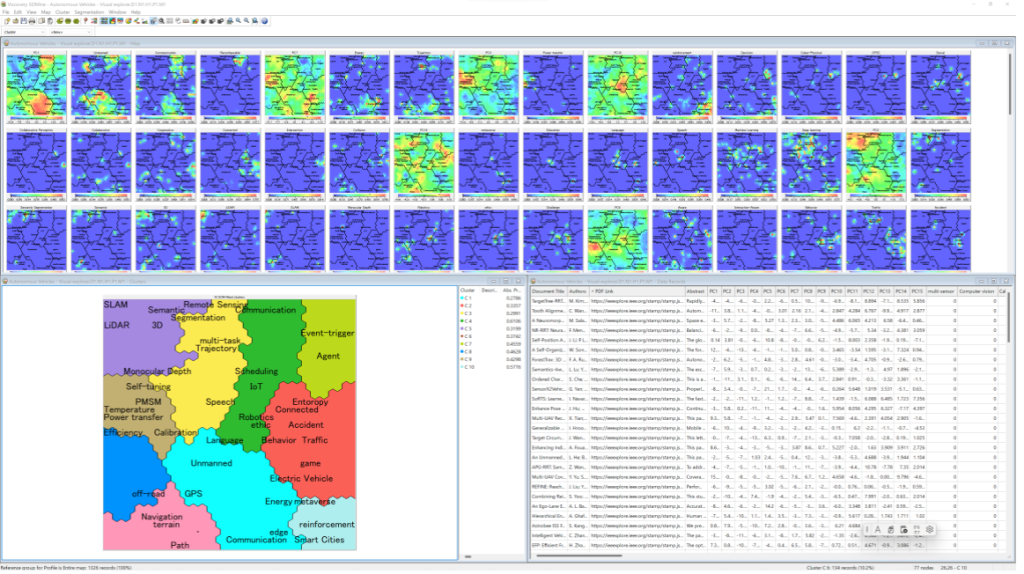
By clicking URLs in Data Records window, you can access PDF documents quickly (if it is in public) corresponds to Node/Cluster/Nearest Nodes/Sllection as you want. (It requires to become Paid E-mail member in order to access to Data Records window.)
Viewer:
You can display this map with free software module of Viscovery SOMine Visual Explorer. Please download English version from here (Windows 10 or higher required). Japanese version is here.
SOM file:
And you can download the map file from here. However please note that underlying data mart is not included, so there is some limitation to explore and analyse it.
If you are interested in this map, you can become “paid E-mail member” of Mindware Innovation Maps, so that you have access to the project file including data mart, and “paid license member can access to full functionalities to mine data which unreduced dimensions. <read more…>